Anorexy
Pairs:
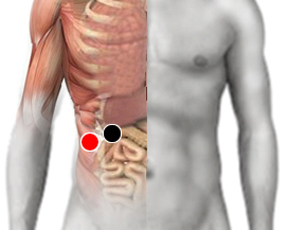
perihepatic - perihepatic
heart - stomach
Generalities:
It is the lack of appetite that leads to the person losing weight and putting their health and life at risk.
It is a disorder of eating behavior that involves a loss of weight caused by the patient himself and leads to a state of starvation. Anorexy is characterized by the fear of gaining weight, and by a distorted and delirious perception of the body itself that makes the patient look fat even when his weight is below the recommended. For this reason, a progressive decrease in weight begins with fasting and the reduction of food intake. It is more frequent in female adolescents.
Anorexy may also be accompanied by Bulimia. In this case the patient is induced vomiting after eating to avoid gaining weight.
Little is known about its causes, although it is estimated that there may be several psychological factors involved such as:
- Self esteem
- Social pressure
- Obesity in the family
- Grief or loss (death of a loved one, divorce ...)
- School failures
- Accidents
- Guilt and shame
- Traumatic experiences, among others.
Within biomagnetism, some pairs have been found that may induce the appearance of this disorder.
Related Pairs:
- Transverse colon - Liver: Vibro Cholerae
- Quadriceps - Quadriceps: Magda
- Clamydia Trachomatis
- Liver - Kidney (R): Cirrhosis hepatic
- Esophagus - Esophagus: Fasciolopsis Burski
- Perihepatic - Perihepatic: Typhus Morganella
- Pylorus - Kidney(L): Amebiasis intestinal
- Temporal (L) - Temporal (L). Polioma, virus
- Temporal (L) - Temporal (R) Typhus exanthematous
- Thymus - Parietal: Rubella